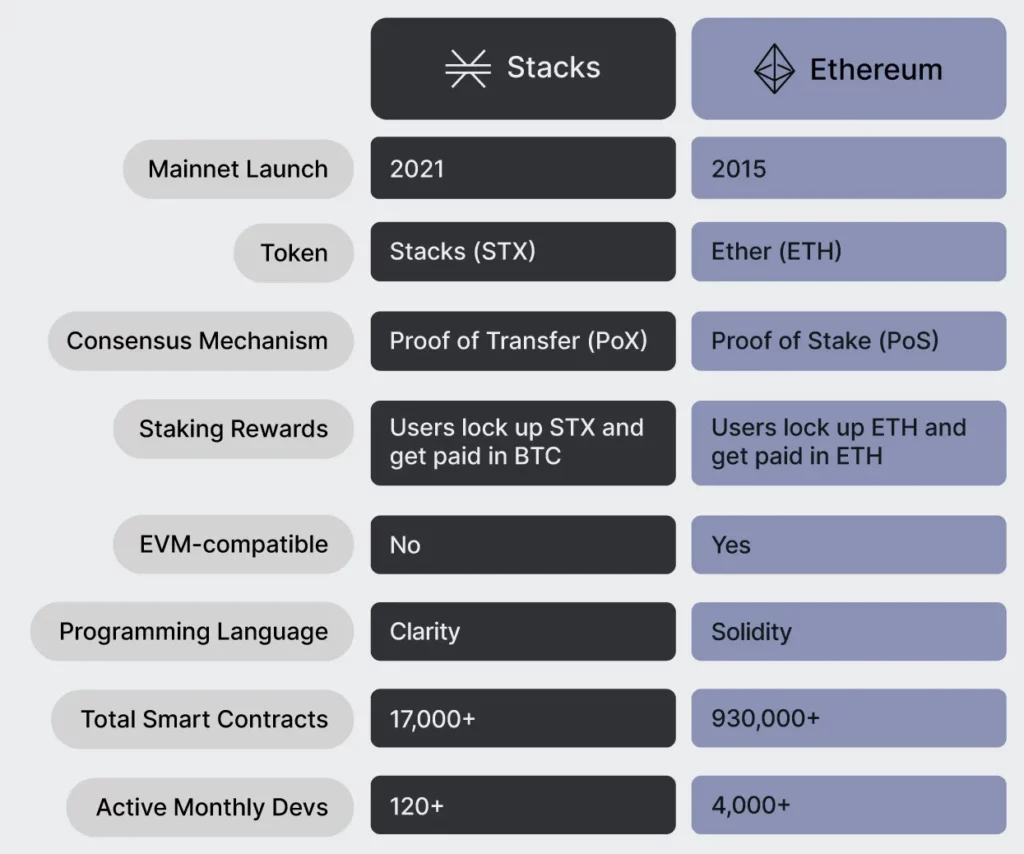
- Stacks is a cryptocurrency project that aims to utilize the full potential of Bitcoin’s blockchain by introducing dApps and Smart Contracts to it.
- Ethereum was the first to introduce smart contracts, with over 900,000 smart contracts launched on its blockchain.
Stacks uses Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) while redefining Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism to secure its blockchain. Ethereum, on the other hand, uses the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Both blockchains work with different mechanisms but enable smart contracts and DeFi app functionality for developers.
Stack and Ethereum Framework
Stacks and Ethereum both apply a different approach in their network’s framework. Ethereum’s blockchain combines its settlement, payment, and programming layers all in one package, while Stacks and Bitcoin are further classified into three layers with their own functionality:
- Bitcoin- Settlement Layer
- Lightning Network- Payment Layer
- Stacks- Programming Layer
This architecture has several advantages, keeping Bitcoin’s blockchain more secure and making the ecosystem more scalable. Instead of customizing the entire functionality in a single layer, the layered architecture approach proves to be more beneficial.
Comparison over Consensus Mechanism
Due to the importance of decentralization, consensus mechanisms provide a way to authorize or validate transactions between different peers, with the ledger recording the version of the truth. The consensus mechanism of the base blockchain is crucial for developers building Web3 applications, as it can affect the scalability and security of the network.
The consensus mechanism used by Stacks and Ethereum is two different protocols:
Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) in Stacks
PoX combines Stacks with the Bitcoin system, leveraging Bitcoin’s competitive security over a decade. PoX redefines Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, allowing users to earn Bitcoin by staking STX for a secure network. It also enables users to earn different cryptocurrencies than those on the network, making the network token a valuable and productive asset.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in Ethereum
PoS works by staking a node’s coins to validate or authenticate a transaction. Unlike proof of work, where mining individuals spend energy to solve problems, PoS miners get incentives simply by staking their tokens to the network. Nodes get randomly selected for validations, and transactions are authenticated until a block is formed.
Privacy And Security
Both Ethereum and Stacks are secure protocols, with any cyber threats tending to affect the smart contract level rather than the entire blockchain. Bitcoin contributes to the high security, control, and reliability of Stacks’ decentralized blockchain.
The node count is much higher in Stacks compared to Ethereum. Both blockchains possess their own level of security, but due to a recent merge of Ethereum with a consensus mechanism, it introduced new censorship and centralization.
Conclusion
While Ethereum was the first to introduce smart contracts, now Bitcoin, with the help of Stacks, provides opportunities for web3 developers to access smart contracts to their full potential, enabling access to decentralized finance and dApps.



